Lei Feng network (search "Lei Feng network" public number attention) by: The author of this article is Hui Chen, general manager of TMT Internet Research Liu Zan.
Before you look at the map, think about a question. Why is Smart Manufacturing and Industry 4.0 the next direction?
Starting from the use of tools by the earliest craftsmen, the material form of scientific and technological progress is basically embodied in the process of manufacturing development. The application of science and technology to manufacturing can best embody advanced methods such as human rational application tools and techniques in pursuit of profit maximization and maximum efficiency. . Therefore, in accordance with the logic of scientific and technological development, manufacturing will inevitably develop toward the stage of information and intelligence. In simple terms, it is very likely that human wisdom has developed to this stage, and no longer does not show that it can no longer demonstrate the higher human capabilities.
Photo 1 : Smart Manufacturing Process PanoramaAs an outstanding pioneer, Siemens Digital Factory in Germany has achieved 75% of its production automation in 25 years, with over 1000 online monitoring nodes on the production line and more than 50 million data collected daily. Each year, 3 billion components are produced, which can be supplied to customers 24 hours a day. The production capacity is 8 times higher than before digitization.
Looking at the numbers alone will feel that basically the core key indicators of smart manufacturing are mentioned, but it is not possible to directly feel where the specific cows are. The HCR Huichen TMT Research Department has compiled a panoramic view of the smart manufacturing process (below), hoping to sort out the relevant parties and influencing factors of smart manufacturing from a global perspective.
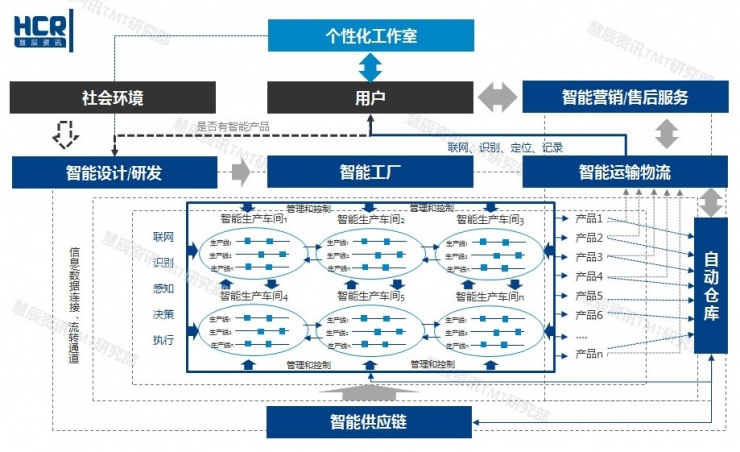
From the above figure, it is not difficult to see that intelligent manufacturing is a systematic project, even if a single point of entry also requires systematic planning and implementation.
Challenge 1: Full connection
Lack of any one node's connection may affect the realization of full automation. How many connections will be involved here? For example, to say that a product that is not very popular nowadays, such as a motorcycle, there are more than 250 parts for only the engine, and there are about 30,000 cars. For the manufacturing process, no one screw can be less, and the smart manufacturing connection is the same. In addition to these, other related information, including the amount of funds, management information flow, logistics information flow, service information flow, etc., need to be fully connected.
In the informationization phase, the biggest problem of the ERP system is that the reverse process is difficult to implement. In addition to the connection points in the intelligent phase, it is also necessary to set up bidirectional monitoring points and production management connection points in the comprehensive connection points. Based on the needs of mass information transmission and multi-node control at a time, separate connections and data flow channels are required to ensure that the entire process is continuous and without packet loss, and the entire process is successfully completed. In addition, whether there is a smart product is a prerequisite for establishing a direct connection with the user.
Challenge 2: Full Control
Smart manufacturing uses data flow as the core, linking all manufacturing and related links. The entire process in the middle is like a “black boxâ€. It is very important to know what is happening at any time and to make artificial corrections and early warning interventions. The interaction design and computational capabilities of each node are the basis for achieving full control. In addition to the control of the links, smart devices (including industrial robots) need to be monitored and controlled. The smart manufacturing production line will replace humans with smart devices to complete the implementation. The coordination of people and machines and the control and management of people on machines are also problems that are more likely to occur in intelligent manufacturing challenges.
Challenge 3: Resource Integration
The social environment and users in the picture are the influencing factors of smart manufacturing. In the intelligent manufacturing stage, the major factory forms are large manufacturing platforms and small personalization studios. The big platform can meet the demand for customization of small batches, and the small studio is more embodied in a more direct and shorter connection with the user. As for the intelligent supply chain, there will also be a large supply chain integration platform to provide fast, “zero inventory†supply for different individual needs. The intelligent manufacturing systemization project must integrate supply chain, production, logistics, service platform, marketing resources, etc. in order to maximize the automation of intelligent manufacturing and maximize production capacity.
Since there are such high requirements for smart manufacturing, we can conclude from the above two paths: One is to take the initiative and then copy the successful experience to other companies in the industry to promote the overall progress of the industry and achieve greater intelligence. manufacture. The other is that the major companies in the industry have integrated related resources and tried to focus all relevant links on this platform to operate as an independent OEM center. It is not difficult to infer that the industry alliances and third parties provide related solutions and data services or will become essential.
In summary, smart manufacturing, even if it has not yet been implemented, is in line with the laws of socio-economic development. It has always been a long-term task. In addition, the so-called challenges have different meanings for companies with different stages of development and digitization, and cannot be generalized.
Figure 2: Smart Manufacturing Data Flow Diagram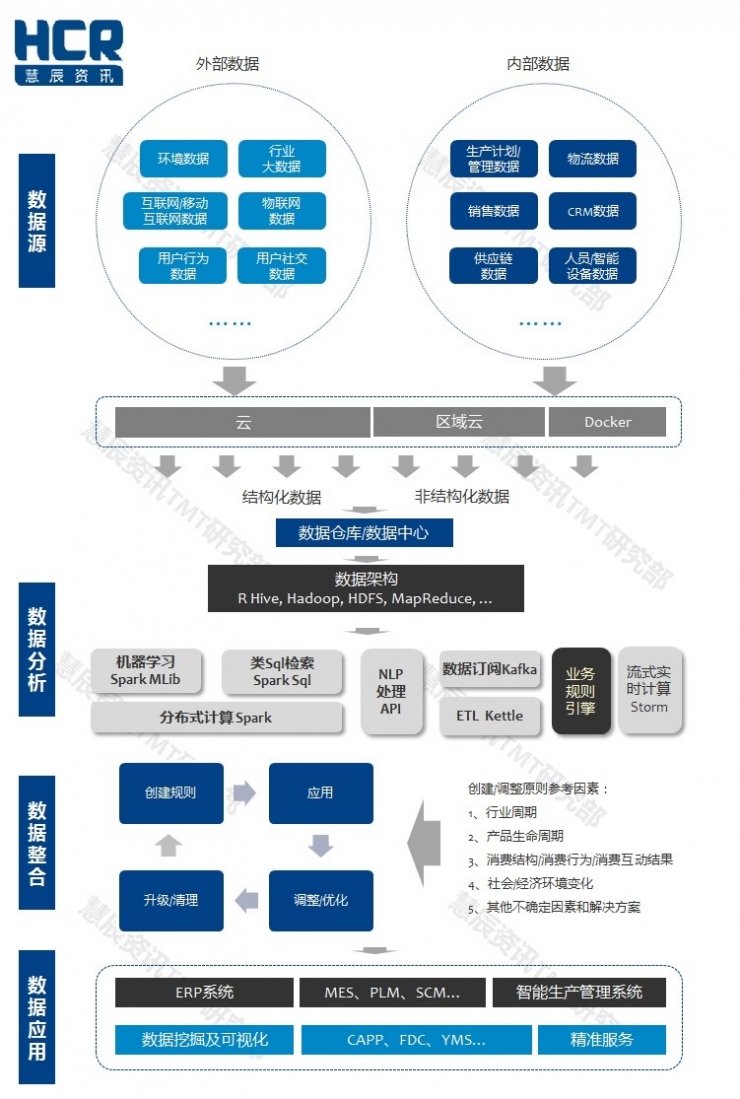
Challenge 4: Data Acquisition and Integration Applications
The collection and integration of large and small internal and external data of enterprises is the basis of smart manufacturing efficiency. The acquisition of data related to smart products will also be the basic data for product upgrades. The ability to acquire and integrate data, especially external environment data, industry data, and user data, is the most cost-consuming and most capable of embodying enterprise resource integration capabilities. The requirements of intelligent manufacturing for enterprise data capabilities include data entry control, data collection methods (new models after crowdsourcing), data center planning and implementation capabilities, data computing resources, and intelligent algorithmic management capabilities.
Challenge 5: Data Transfer Channels Interact with Time
This involves the establishment of multi-node protocol standards for network channels and networks. Multi-node interaction, monitoring and control, as well as cross-industry, cross-domain, cross-product and other multi-scenario requirements require the establishment of new, systematic, and unified protocol standards. In addition to the overall architecture and the basic Internet of Things, at least the same Industry (domain) began to refine and establish a unified standard. In addition, the current network resources clearly cannot support the development requirements of smart manufacturing, whether it is from the bandwidth (real-time data capacity) or network speed requirements. Now everyone puts hope on 5G and looks forward to the new Internet of Things standards. What else can you say? Look forward to it.
Challenge 6: Creating and Opening Multiple Scenes of Data Models
A statistical method to eat all directions, a data model will not occupy the whole world of happiness. Although big data and intelligent algorithms are the ones, the real test of smart manufacturing is the establishment of data structures and models based on different scenarios and conditions, as well as the opening of data and data models under multiple modes and scenarios. Any thing will be biased, even if there is no deviation, it is necessary to make timely adjustments according to external changes, and it is also impossible to completely rely on the machine to interpret and summarize the data. Therefore, professional analysts who have insight into the development of the industry and business lines are required to adjust, optimize, upgrade, and abolish the rules.
In the future, data will become the lifeblood of smart manufacturing, data collection, storage, rapid deployment, model building, rule creation and integration, calculation and application. Each link is closely related to connection, control and automation . HCR Huichen TMT Research Department believes that data service capabilities will become an important development area and direction for third-party services in the future. Data experts and engineers will become hot professionals.
Some experts said that even from the point of view of the three major industries, the Internet has been devoting itself to influencing the tertiary industry for the past few years. It will inevitably be exerted in agriculture and industry (manufacturing) and will have great prospects.
But judging from the difficulty of the challenge, relying solely on the power of business is not enough. At present, the world's top two economies have taken action in this area. The US government announced on June 20 a bill that will promote the revival of US manufacturing by stimulating the method known as "smart manufacturing." The Institute of Intelligent Manufacturing Innovation is the ninth manufacturing center promulgated by the Obama administration and will initiate five regional manufacturing innovation centers within the United States. Each center will focus on relevant technology transfer and labor development in the region. In May of last year, the Chinese government also issued the “Made in China 2025â€, a strategic plan for the development of manufacturing-powerful countries in the medium and long term. It is expected that the key areas of manufacturing will be fully intelligentized in 2025, the pilot demonstration project will reduce operating costs by 50%, and the production cycle will be shortened by 50%. The defective product rate is reduced by 50%.
Policy-driven, talent pool, business investment, and scientific research support are all necessary conditions. The development and application of new technologies will inevitably have to be fought innumerable pits. How many heroes and lords will sigh and sigh unacceptably, they can only turn a blind eye to those who have seized the best match between technology and the market to become heroes, and continue to turn a blind eye. Take a mud pit. For the development of smart manufacturing, what is needed most is for those brave warriors who dare to go through one pit after another, pat the mud, and sum up lessons learned to continue the next round of trials. Without the determination to meet the challenge, there is no chance of welcoming the victory.
Hui Chen TMT Internet Research analyst team, research smart +, focus on intelligent hardware, artificial intelligence, cloud computing, business intelligence and related fields. WeChat public number: Intelligent Institute.
Medical Grasper Instrument,Grasper Surgical Instrument,Medical Grasper,Laparoscopic Grasper
Dragon Crown Medical Co., Ltd. , https://www.dragoncrownmed.com