1 Introduction
The rapid growth of in-vehicle infotainment equipment and the rise of Advanced Driver Assistance Systems (ADAS) have created a need for more efficient interconnections between automotive interiors. By taking advantage of other technologies, Ethernet is the automotive network. The ideal choice.
Plastic optical fiber (POF, PlasTIc OpTIcal Fiber), a well-known transmission medium in the automotive industry, can now provide gigabit transmission capacity, making it the perfect solution for future automotive Ethernet networks and point-to-point link applications such as camera lenses. .
2 car Ethernet network
Cars have quickly become an extension of the family, and infotainment systems are increasingly becoming the basic equipment for connecting neighboring devices and other vehicles in new cars. Internet and car infrastructure are becoming the future industry standard for car equipment.
Similarly, driving assistance is also the main way to provide a safe corner of the car without a dead end, avoiding traffic accidents, because the car and infrastructure can be designed to achieve this goal without being mistaken or deliberately affected by driving, ADAS will join other passive And the active system becomes the standard car equipment.
These feature-rich infotainment and driver assistance systems will dramatically increase communication bandwidth requirements and increase the complexity of automotive networks, as more complex automotive networks can affect reliability and maintainability, infotainment systems and driver assistance systems. The increase creates demand for new network solutions that go beyond point-to-point links or ring topology that currently do not provide inter-car communication.
2.1 Ethernet provides scalability and flexibility
The Controller Area Network (CAN) is a communication protocol for the electronic architecture of the past 30 years. It is no longer able to meet the needs of future automotive architectures. On the other hand, Ethernet can provide a new generation of in-vehicle networks. The scalability and flexibility that the architecture requires.
For most automotive OEMs, scalability is a key feature that can be used on multiple automotive production lines by means of a platform that is supported by network technologies that allow each car to be customized separately.
High flexibility is also a key feature that allows automotive OEMs to offer multiple vehicle customizations without the need to change the network. The network configuration will automatically adapt to the specific equipment in the car, and the car manufacturer does not need to specialize in each model. Perform network configuration.
2.2 Ethernet application of upper and lower communication layer
Ethernet can be used as the lower communication layer of the standardized IP diagnostic interface. It is developed by ISO 13400 DiagnosTIc CommunicaTIon over Internet Protocol and is expected to be adopted by most automotive OEMs worldwide. This interface based on the same IP protocol as the Internet simplifies the diagnosis of in-vehicle systems. As a lower layer technology, Ethernet can be smoothly interfaced with IP, which is one of the reasons why it is currently widely used in Internet connection networks.
Ethernet also brings seamless connection with other upper layer protocols. For example, it can assist video and audio synchronization or secure transmission of timely information, and audio and video synchronization (AVB protocol stack, IEEE 802.1 Qav, which is very important for infotainment networks). 802.1 AS, 1722) ensures the synchronization of video and audio between different screens and speakers in the car.
Similarly, timely information provided by the Precision Time Protocol Stack (IEEE 1588v2 and 1722) is very important, especially for ADAS, which ensures that information can reach its destination without delay to meet the requirements of security applications.
2.3 layered architecture of the Ethernet backbone
All major automakers agree to the benefits of splitting the car into different functional blocks. In this new structure, the car will work together and share information in several different areas, such as powertrain, body control, transmission. And security systems, etc.
In each field, the form of connection used will be based on the functions to be performed and the needs of each domain. Typical cross-domain networks will be based on FlexRay, MOST, Ethernet (first generation based on BroadR-Reach), CAN or LIN, etc. .
In order to meet the new demands brought by the layered architecture, a broadband network will be required for reliable communication between all areas. Currently Ethernet seems to be the best choice. However, the best physical layer of gigabit speed is still under discussion. Among them, the POF-based optical physical layer can provide 1Gbps bandwidth requirements to meet the requirements of current and next-generation systems, while at the same time bringing the advantages of lower cost and lighter weight.
Figure 1 shows the centralized architecture currently in use. In this architecture, a single central gateway (CGW, Central GateWay) provides CAN cabling, LIN cabling, FlexRay cabling, and MOST cabling.
In a distributed backbone architecture, the automotive subsystem is differentiated into a single network technology, such as a CAN or Ethernet zone group, or a mix of technologies.
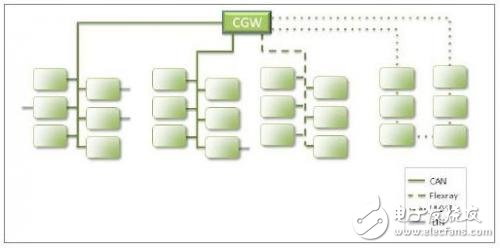
Figure 1: Centralized architecture
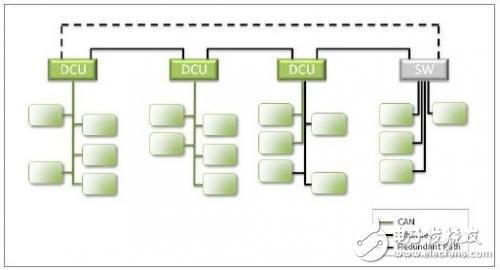
Figure 2: Daisy chain backbone with optional redundant paths
Through the new domain-based architecture, it creates the backbone requirements for connecting all domain control units (DCUs) and exchanges between each domain. Although there are several backbone structures to choose from, it seems that the most competitive is to provide Select the daisy chain backbone of the redundant path.
Since all areas are connected through a single backbone, its size must be automatically adapted to the amount of data movement between the domains. For future projections, ADAS and infotainment systems plus each area of ​​the car will require 1 Gbps. backbone.
3 unique challenges in automotive applications
The physical layer of the network technology used by the automotive network must meet the unique challenges of the automotive environment and cannot significantly increase the cost. The final cost of the system is determined not only by the performance itself, but also by the environmental conditions of the vehicle, which in most cases is Will increase the final cost.
The challenges facing automotive networks include:
â—Vibration
The network technology used must be able to withstand the vibrations that the car has in a continuous travel environment. Vibrations can affect all of the mechanical components and are particularly susceptible to damage to the electrical connectors, thus placing stringent restrictions on cables and connectors.
â—temperature
The temperature range in different areas of the car will vary depending on the location of the network, and the maximum temperature in most automotive areas is approximately 105 °C.
â—weight
The use of weight as a network vehicle is important because it directly affects fuel consumption and costs, as well as associated carbon emissions.
â— Cost predictability
The copper-based physical layer is affected by the unpredictability of copper prices. Copper prices have risen sharply in the past 10 years, and the inability to estimate costs steadily has become a negative factor affecting copper-based cable solutions.
â—Electromagnetic compatibility (EMC, ElectroMagnetic Compatibility)
Electromagnetic radiation and interference are a major challenge for automotive networks, and electrical-based communications, such as the use of copper as a physical layer, are particularly susceptible to electromagnetic interference (EMI, ElectroMagnetic Interference).
â— length
The typical length of a car network is about 5 meters, and some networks may extend to 15 meters. Any communication technology used in a car network must be able to provide sufficient signal-to-noise ratio (SNR) while covering these length ranges. degree.
Fully Automatic Washing Machine can make your clothes more clean in a very convenient way. With PCB control, different procedures can choose more ways to wash different clothes. Nowadays fully automatic washing machines are widely used in home, hotels and laundry shops.
Our well-equipped facilities and excellent quality control throughout all stages of production enable us to guarantee total customer satisfaction. Besides, we have received CE, CB, RoHS and CCC certifications.
As a result of our high quality products and outstanding customer service, we have gained a global sales network reaching America, Asia, Europe, Africa, the Middle East and other countries and regions.
If you are interested in any of our products or would like to discuss a custom order, please feel free to contact us. We are looking forward to forming successful business relationships with new clients around the world in the near future.
Fully Automatic Washing Machine
Washing Machine,Fully Automatic Washing Machine,Mini Automatic Washing Machine,Fully Automatic Washing Machine With Dryer
Ningbo Banshen Electric Appliance Co., Ltd , https://www.banshendq.com