Solving complex challenges requires advanced and innovative technology. Electromechanical relays have been around since the early days of the telegraph, yet no alternative switching solutions fully meet the diverse demands of today’s markets—especially in test and measurement, communications, defense, healthcare, and consumer electronics. These industries require high-performance, reliable, and compact switching solutions.
As an example, test and measurement users are pushing for the smallest standard test solutions possible, with high parallel testing needs across a wide frequency range—from 0 Hz/dc up to hundreds of GHz. However, traditional electromechanical relays suffer from limitations such as narrow bandwidth, limited lifespan, low channel count, and large form factors, which are becoming increasingly restrictive for system designers.
Microelectromechanical systems (MEMS) switches offer a groundbreaking alternative that can replace relays and elevate performance to new levels. With state-of-the-art MEMS manufacturing capabilities, Analog Devices is now producing high-performance, fast, small MEMS switches that deliver mechanical durability, low power consumption, and electrostatic discharge (ESD) protection.
**MEMS Switch Technology**
The core of ADI’s MEMS switching technology lies in the use of electrostatically driven micromachined gold cantilever beam components. Essentially, these switches function like micro-scale mechanical relays, using metal-to-metal contacts powered by high-voltage DC static electricity.
Figure 1 shows a close-up view of a single MEMS switch cantilever. It features five parallel contacts and a hinge structure with a gap below. This design is used in the ADGM1304 SP4T MEMS switch and the enhanced ESD-protected ADGM1004 version.
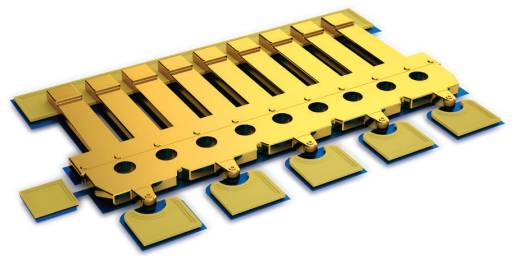
**Figure 1. Close-up of a MEMS Cantilever Switch Beam**
To drive the switch efficiently, ADI has developed a companion driver IC that generates the necessary high DC voltage. This ensures fast and reliable operation while extending the device's lifetime and simplifying integration.
Figure 2 illustrates a MEMS chip and driver IC packaged together in an ultra-small SMD QFN package. The combined driver consumes only about 10 mW—10 times less than typical RF relay drivers.
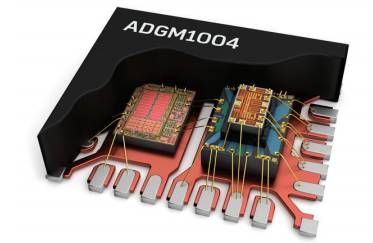
**Figure 2. ADGM1004 Enhanced ESD Protection MEMS Switch**
**Integrated ESD Protection**
The ADGM1004 MEMS switch includes integrated solid-state ESD protection, enhancing RF port ESD performance. Its Human Body Model (HBM) rating reaches 5 kV, setting a new industry benchmark. This proprietary technology ensures strong ESD protection without compromising RF performance.
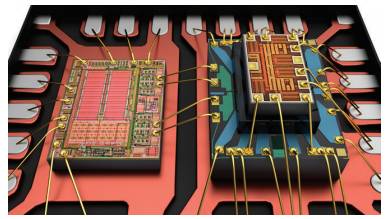
**Figure 3. ADGM1004 Driver IC and ESD Protection Chip**
ADI combines three proprietary lithography technologies with advanced assembly and MEMS capping techniques to achieve this level of performance.
**RF and 0 Hz/DC Performance**
MEMS switches excel in delivering 0 Hz/dc precision and wideband RF performance in a compact surface-mount package. Figure 4 shows the insertion loss and isolation performance of the ADGM1004 SP4T MEMS switch. At 2.5 GHz, the insertion loss is just 0.45 dB, and it remains under –3 dB up to 13 GHz. The RF power handling capability is 32 dBm, with a third-order intercept point (IP3) of 67 dBm across the entire frequency range, without degradation at low frequencies.
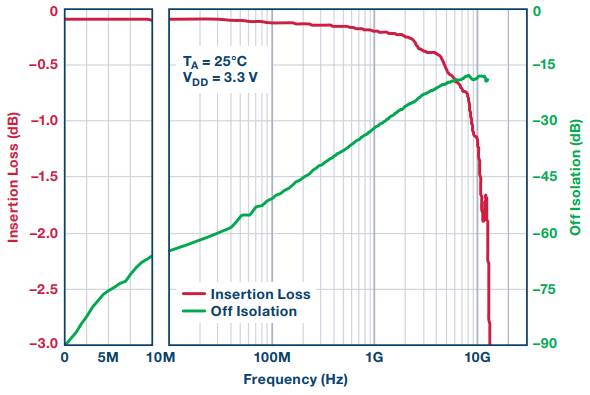
**Figure 4. ADGM1004 MEMS Switch RF Performance Linear Scale <10 MHz**
Table 1 highlights key accuracy specifications, including a 5 kV HBM ESD rating—an improvement over the 100V HBM of the previous ADGM1304 model.
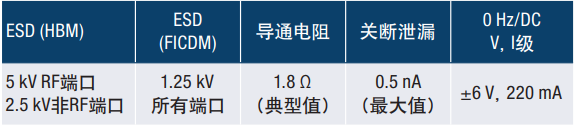
**Table 1. ADGM1004 Accuracy Specifications I**
Table 2 provides additional performance data, emphasizing the switch’s reliability and precision.

**Table 2. ADGM1004 Accuracy Specifications II**
Small size is a critical requirement across all markets. Figure 5 compares the ADGM1004 SP4T MEMS switch to a typical DPDT electromechanical relay. The ADGM1004 is up to 95% smaller.

**Figure 5. ADGM1004 MEMS Switch vs. Electromechanical Relay**
Finally, the thermal switching life of the ADGM1004 was tested under RF power transfer conditions. At 2 GHz and 10 dBm, the average number of cycles before failure (T50) was 3.4 billion.
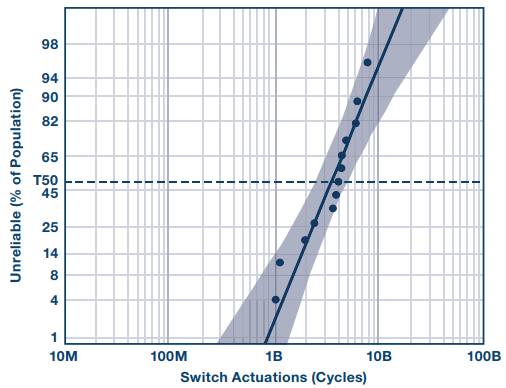
**Figure 6. Lognormal Failure Probability at 95% CI for 10 dBm RF Signal Hot-Swap**
The enhanced ESD protection of the ADGM1004 significantly improves usability while maintaining excellent performance in both RF and 0 Hz/dc applications. ADI’s MEMS switching technology offers world-class bandwidth starting at 0 Hz/dc. Compared to RF relays, MEMS switches are up to 95% smaller, 10 times more reliable, 30 times faster, and 10 times more power-efficient. The ADGM1004 adds a powerful new option to ADI’s already robust switching portfolio.
Connector 2.00Mm Pitch,Ph Connector Accessories,Ph Connectors Accessories,Strip Wire Connectors
YUEQING WEIMAI ELECTRONICS CO.,LTD , https://www.wmconnector.com