When the Hypertext Transfer Protocol (HTTP) was invented, no one could expect the advent of modern Web 2.0 infrastructure with modern browser capabilities. In modern life, we conduct "surfing the Internet" several times a day. We communicate through web tools like Facebook, MySpace and Flickr, and don't forget to use regular email. We can shop online with peace of mind, thanks to the secure extension of the original protocol, which is now called HTTPS (the "Security" section has been added). At the same time, the organic machine (M2M) application runs in the background, completing tasks such as database update and meteorological data collection.
This article refers to the address: http://
All of these systems are implemented based on the server-client model. That is, there is a client (such as a browser) and a server that provides content or collects information. Initially, the server is assigned one (or several) IP addresses, and the server software provides the content to the client. When you create a new Site, the server software will have the allocated resources and dedicated storage. Normally, this mode works well when the load is stable (ie, the fluctuation is not large). For example, if I know that a server can provide 10 million web pages per second (assuming communication bandwidth is available), and the other party knows the maximum "page hit rate" of each hosted website, then he can calculate the server. The load is maintained in order to maintain peak performance for customers (hosting customers and using customers).
The impact of Web 2.0
When everything on the site is static (that is, the content rarely changes), the run will be pretty good. An online dictionary with only word query functionality (no video, music, etc.) is a good example. In this case, it is easy to calculate the load. According to statistics, not everyone in the world wants to query the definition of the word "Stochastic" at the same time... You may think that the load will change at different times of the day, but on a global scale, some people are always doing it. Queryed.
The Web protocol works by opening a session with the server, receiving content, and then terminating the session, freeing resources from the server for use by other tasks. Now all the "content" is in the browser. So when you look up a word, its definition and any graphics are sent back to you, and you can read at your own pace. The server will go to other things.
However, this is no longer the case. What happens when you download music videos? The server is no longer just providing a web page and then moving on. It is now working hard to transfer 40 megabytes of files to your machine. By adding an embedded player to the web page, the server will send the video stream to the client in real time. In this case, the load is still statistically monitored and the website can be modified. As popularity or demand increases, websites can be moved to dedicated, single-domain-only servers.
That was the case with Web 1.0. The problem with Web 2.0 today is that most of what we do is done on the server side. For example, Google Docs is a complete file editing and archiving system on the server side. It uses a computer's browser as a user interface tool, but rarely uses customer resources. Now, when people start using the network, more work is done in the background. The interaction between the server and the client is increasing, and unless measures are taken to ensure adequate resources, this will cause the server's load to fluctuate drastically and cause performance degradation.
Seeking a solution
In the past, an energy-efficient approach to preventing website crashes was to load the largest load of statistics into a domain. In most cases, the load on these servers may only reach 40-60%, but will reach 100% during peak hours, but the site will continue to work effectively. People quickly realized that most of the time the server did not reach the maximum load. They only work part-time until the peak load comes – and the time of this peak is not always known. For example, on any given day, traffic to a news site may be maintained at a normal level. And when an emergency occurs, if everyone checks the photos or videos related to them online, it may lead to website crashes.
The best solution is to "virtualize" the server—that is, to create software that looks like a dedicated server, but, if needed, can dynamically move to more resources during processing. When the high load disappears, the software can "slim" the server by merging more sites into one machine (the blade in a modern server). Other unused blades can go into standby, greatly reducing the power consumption of the center. Adopting this new method not only reduces the power consumption of the server, but also reduces the HVAC cost of heat dissipation, thereby reducing the energy cost of the server room.
Impact on the server
This is a major move towards the “greening†process of data centers and server farms. Energy consumption is reduced, but often software also affects hardware (and vice versa). What impact does load shedding have on the system hardware and the surrounding infrastructure?
The power of the blade server should be observed first. In general, there are two sets of redundant power supplies in the blade server to convert the civilian Power Supply into a DC bus. The busbars are routed along the length of the backplane (where all the blades are inserted) and each blade has its own power regulator to provide the correct voltage and current. In larger systems, the DC bus can be routed along the height of the rack to serve multiple sets of blades stacked on top of other systems.
When designing a power supply, you need to have a specification as a target load. This tells the designer where to place the highest energy efficiency conversion when selecting components. The design equation provides the component values ​​that the system will work most efficiently. This is a fixed point, so increasing or decreasing the load (in most cases reducing the load) will change the efficiency curve. If the peak load efficiency of the target load is 92%, then reducing the load to 25% of the target requirement may result in a efficiency drop of 75%.
Power supply designers suddenly face a new challenge of providing an efficient power supply that can operate over a wide load range. Modern switching power supplies use high-power FET transistors to "switch" the power supply, using pulse width modulation (among other methods). The output of these techniques presents a complex waveform with an average of the new lower voltage. A high-power filter made of inductors and capacitors smoothes the output waveform while providing a clean DC voltage. The output is monitored by the controller and the FET switching is changed to maintain a stable output as the load and input change.
Field effect transistors, inductors, and capacitors should all be selected to meet load specifications, and their values ​​cannot be dynamically changed once they are fixed in the line. Therefore, if the load falls below the design specification, the energy will be lost due to the loss of these components. One solution is to build a multiphase converter. In high-current power supplies, such as those in a motherboard that provides a core voltage to a processor in a personal computer, it is very common to set up three or four power supplies that work together—each power supply alternately supplies power to the load.
The advantage of this topology is that when the load is reduced, some phases can be turned off, while the remaining phases are expanded to replace the missing phase (see Figure 1). This increases the complexity of the power supply, which is used to ensure that its output does not change during the transition period of phase increase or decrease. All power converters work near peak efficiency or are turned off. Applying this approach to large DC bus power supplies enables blade servers to operate efficiently over a wide load range. However, in order to cope with these dynamic loads, power supplies are becoming more and more complex.
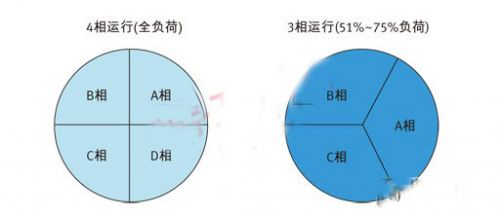
Figure 1 - Phase change with load
Impact on infrastructure
As in the case of power supplies, the communication infrastructure that carries the information is also affected. Each blade server communicates by connecting one or more Gigabit Ethernet to a switch. Physical layer devices in servers and switches consume many watts of power and can accumulate quickly. If a blade server is placed on standby, the physical layer device is usually not turned off - the link remains, but the call has stopped. In most cases, this does not significantly reduce the energy consumed by the physical layer device (PHY) because it still needs to maintain the link. Even if the physical layer device (PHY) on the server side is shut down, the physical layer device (PHY) on the switch side must continue to boot up to monitor link activity - which in turn leads to energy consumption.
Various methods are currently being taken to solve this problem. Physical layer devices (PHYs) that can be switched to standby or intentionally placed in a low-power state when the link disappears will reduce energy consumption. The Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers (IEEE) has a working group called the 802.3az Task Force. The goal is to develop a protocol for the new physical layer device (PHY) that reduces power consumption and keeps the link active when usage is low.
Another approach is to simply limit the semiconductor process itself. The CMOS process power consumption is linear with the frequency and exponentially related to the supply voltage (see Equation 1).
Equation 1 – CMOS energy consumption ![]()
In the past, techniques such as dynamic voltage regulation in personal computer processors have been used to reduce these losses. Today, the more modern technology is called adaptive voltage regulation or AVS, which is used by National Semiconductor to introduce physical layer devices such as the 10G base-T Teranetics TN2022. Basically, AVS technology continuously monitors the performance of the internal process of the device and automatically adjusts it by adjusting the supply voltage. This technology can save 20% to 50% energy compared to a fixed supply voltage. In addition, it compensates for temperature and process variations (aging) during operation. This technology, combined with other technologies, can significantly reduce the energy consumption of infrastructure applications and automatically adapt to load changes due to server access or exit from the network.
in conclusion
So, can other situations happen? A large number of netbooks with low processing power are pushing more resources back to the server. Soon, there may be very little software or disk storage stored on these computers - most files will be stored in "virtual". All traditional software tools used to generate and share documents or presentations will be placed on the server.
In addition, virtual games are on the rise. Most gaming computers require extremely high performance calculations to provide realistic scenes depicted in these games. This may turn to the server side and only send live video streams to the client computer. This may enable low-performance netbooks and other computing devices (including handheld mobile devices such as the iPhone) to play high-performance games.
Human mobility, mobile development changes will return more resource requirements to the data center and infrastructure. As network activity has a wide range of volatility, virtualization will continue to achieve energy savings, while hardware will need to find new ways to adapt to changing loads.
48V Switching Power Supply are 100% PC and brand new. All our power supply adapters have over voltage protection, over temperature protection, short circuit protection, also meet CE ROHS FCC PSE UL KC standard with PFC and 1 year warranty. Maybe we are not the cheapest price in China, also we are not the highest quality in China, but we are your right vendor for power supply business in China. Because we always trust that quality is the soul of an enterprise, and we are the only supplier who can offer you confidentiality agreement in China.
48V Switching Power Supply,48V Dc Power Supply ,Power Supply 48V,48V Power Supply
Shenzhen Pengchu Industry Co., Ltd , https://www.pc-adapters.com