The oscilloscope can observe waveforms through various view modes. There are two major categories: YT and XY. The YT mode can be further subdivided into normal, large time base, scrolling, etc. Which mode should be selected when observing signals It is most appropriate, and there is a correlation between different modes. This article takes you in-depth in-depth discussion of the ways, advantages and disadvantages of each mode display, to help you quickly and accurately find the right mode to observe the signal.
YT mode
The YT mode is the most common in oscilloscopes. Its coordinate system Y-axis is the channel input signal. It is up and down, the reference ground is zero, the X-axis is time, the left is negative and the right is positive, and the trigger point is zero. The YT mode can be further subdivided into ordinary, large time base, scrolling, Zoom, and interpolation modes, which are described in detail below.
1, the normal mode
The normal mode is the most common. The oscilloscope generally works in this mode. Its characteristics are as follows: the sampling is divided and independent. There is a dead zone between the samples. The trigger condition can be set. The waveform is output after the sampling is completed. Stable display.
Advantages: It is suitable for observing periodic signals, eye diagrams, and low-probability anomaly signals, which can perform powerful processing on data, such as measurement, search, and decoding, as shown in Figure 1.1.
Disadvantages: There is a dead zone between samples, which will lose certain data and can sometimes be fatal. When the horizontal time base is large, the waveform refresh is slower because the sampling time is longer.
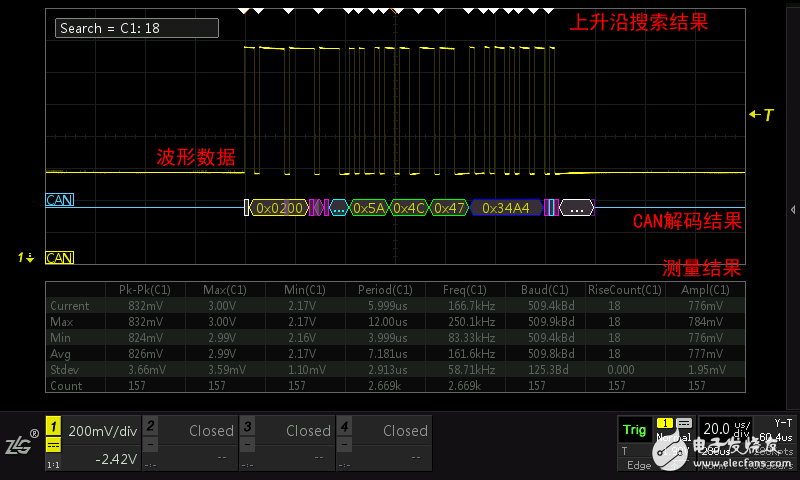
Figure 1.1
2, large time base mode
The large time base mode is similar to the normal mode. The only difference is that the waveform starts to output after the trigger, and the sample is output before the end. This mode inherits all the advantages of the normal mode, and improves the disadvantage that the waveform output is too slow when the horizontal time base is large, so it is called the large time base mode.
Tip: When the base is small, it is meaningless to output while sampling. Because the human eye can't keep up with the refresh rate, the normal mode and the large time base mode will automatically switch according to the horizontal time base. For example, when the horizontal time base of the ZDS2000 series oscilloscope is greater than or equal to 100ms/div, it will automatically enter the large time base mode as shown in Figure 1.2.
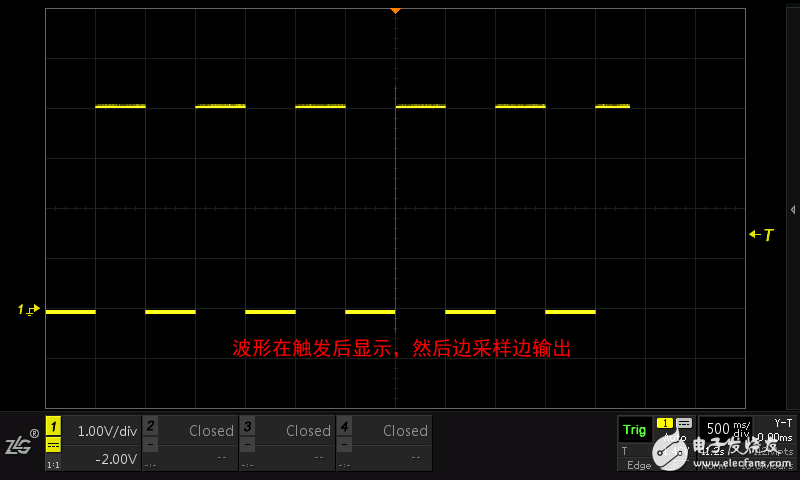
Figure 1.2
In order to better show the edge-sampling output, the large time base mode also provides a refresh comparison with the previous frame data, allowing you to better observe the changes in the input signal as shown in Figure 1.3.
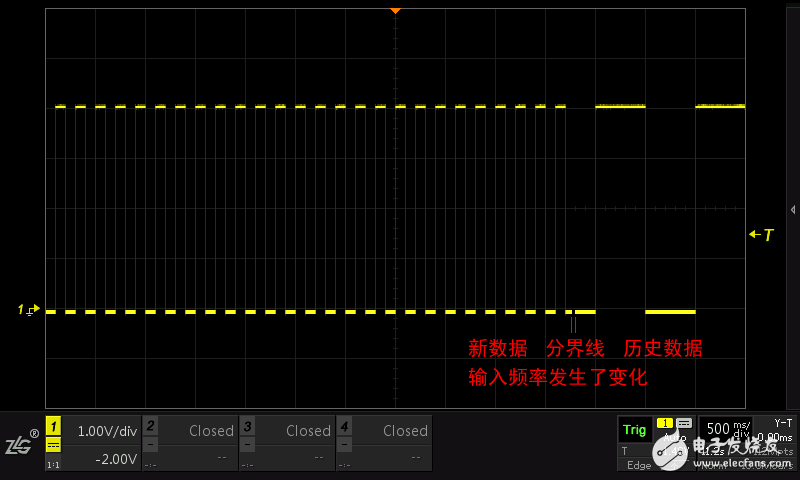
Figure 1.3
3, scroll mode
The characteristics of the scroll mode are as follows: continuous sampling, no sampling interval, side sampling, no trigger setting, the waveform is always scrolled from right to left as shown in Figure 1.4.
Advantages: No dead zone is sampled, and it is displayed in real time without losing data. However, it should be noted that too low a sampling rate will result in the data being meaningless, so it is important to select a deep storage oscilloscope as shown in Figure 1.5. The deep memory waveform is not distorted and perfectly reconstructed.
Disadvantages: The waveform cannot be displayed stably, there is no concept of triggering, and the low probability signal cannot be automatically recognized.
Tip: Why is the waveform scrolling from right to left in scroll mode? Because the time axis defined by the YT mode is left negative right positive (the left side is the new data on the right side of the old data), the newly collected data must be increased from the right side, and the old data is removed from the left side of the screen, so A scrolling display from right to left is formed.
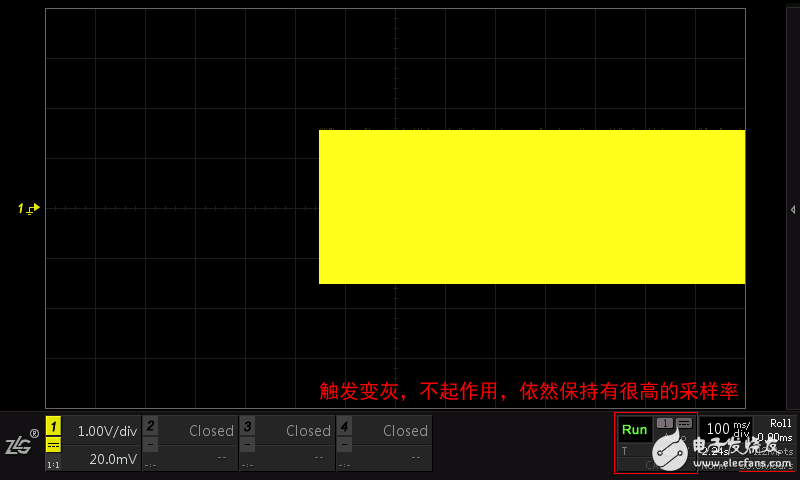
Figure 1.4 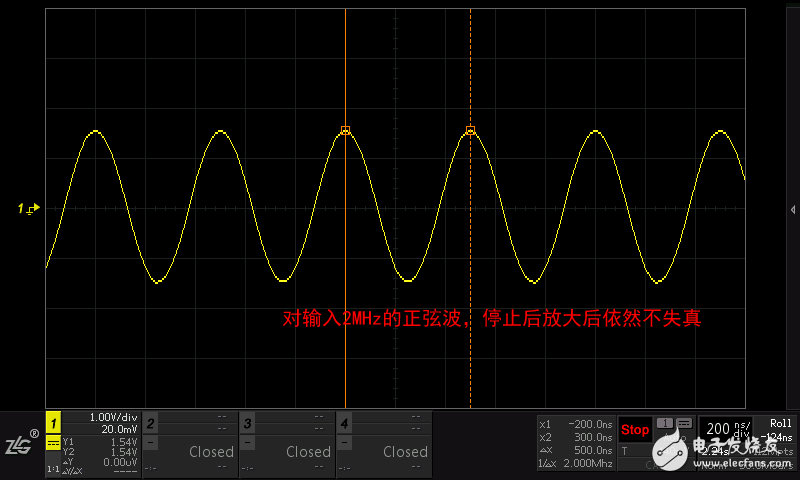
Figure 1.5
4, Zoom mode
The Zoom mode is to solve the problem that the horizontal time base is too large and the waveform display tends to be dense. This mode provides another sub-timebase window, which can view the locally amplified waveform of the main time base, so that the user can view the details as shown in Fig. 1.6.
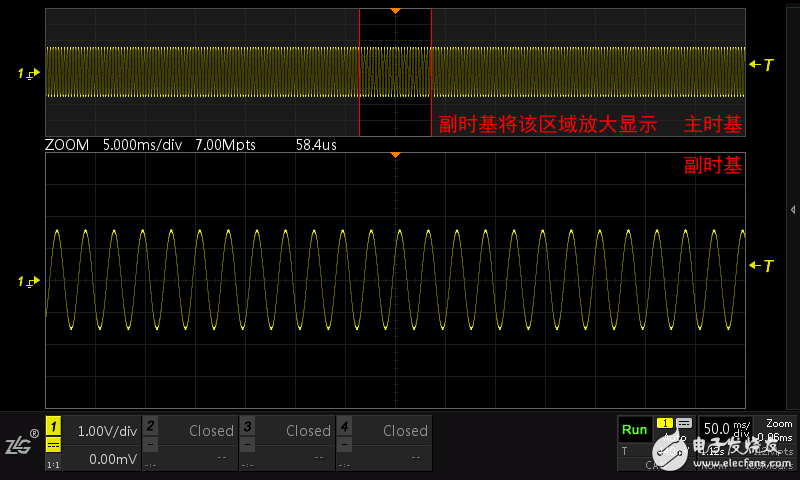
Figure 1.6
5, interpolation mode
Interpolation mode is a special mode when the number of screen points is less than the resolution. Due to the large gap between the two original sampling points, it is usually processed by some methods, and the following three processing methods are commonly used: sinusoidal interpolation, linear interpolation, and original point display.
XY view mode
The XY view mode is to turn off the time base, and use the input of another channel as the horizontal signal to observe the relationship between the two signals. This kind of graph is called Lissajous figure, which can easily observe two signals. The relationship between frequency, phase and amplitude is shown in Figure 1.7 and Figure 1.8.
This mode has gradually weakened in modern math oscilloscopes, because the method can only evaluate a rough value, the error is large, and the powerful measurement function provided by the math oscilloscope can directly yield accurate results.
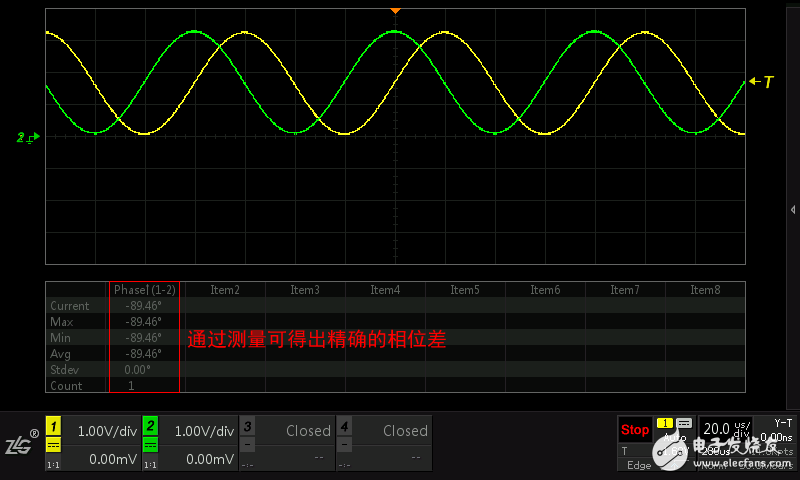
Figure 1.7 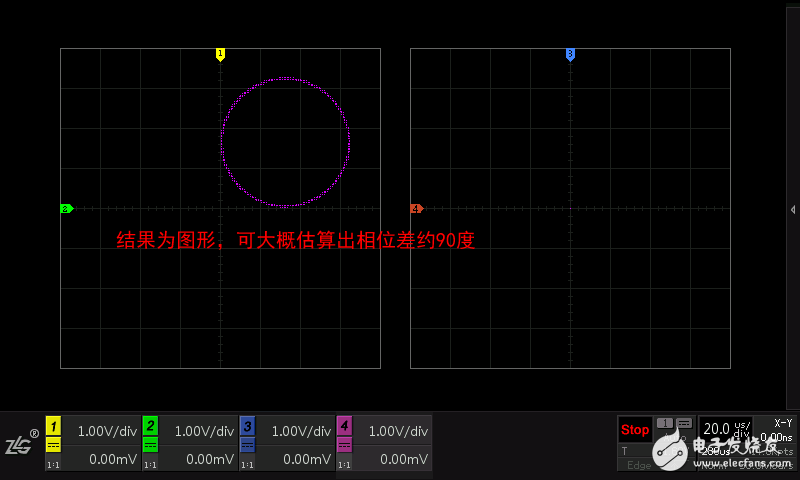
Figure 1.8
3.6V-3.7V Li-Ion/Polymer Battery Pack
5V & 6V Regulated Li-Ion Pack
7.2V-7.4V Li-Ion/Polymer Battery Pack
10.8V-11.1V Li-Ion/Polymer Battery Pack
12V - 13.2V Regulated Li-ion/Polymer Battery Pack
14.4V-14.8V Li-Ion/Polymer Battery Pack
18V-18.5V Li-Ion/Polymer Battery Pack
21.6V-22.2V Li-Ion/Polymer Battery Pack
25.2V-25.9V Li-Ion/Polymer Battery Pack
28.8V-29.6V Li-Ion/Polymer Battery Pack
36V-37V Li-Ion/Polymer Battery Pack
46V-54V Li-Ion/Polymer Battery Pack
Li Ion Battery Pack,Lithium Ion Battery,18650 Li Ion Battery Pack,Panasonic Li Ion Battery Pack
Asarke Industry Co., Limited , https://www.asarke-industry.com