1 Introduction
This article refers to the address: http://
In recent years, the market environment of the communications industry has undergone tremendous changes. The Internet trend of communication services is becoming more and more obvious. The telecommunications networks are increasingly channelized and the telecommunications services are becoming increasingly virtualized. Companies without networks can provide more and more through the use of network channels. The more communication services, the traditional telecom operators rely solely on providing simple voice and data communications to gain profitability models are increasingly difficult to sustain, have turned to "information services."
On the other hand, with the rapid development of electronic technology, more and more functions are integrated into mobile phones, such as media playback, games, photography, navigation, etc., mobile phones are more than just a communication tool, but increasingly become a personal synthesis. Entertainment and information terminals. How to expand the functions of mobile phones, in addition to traditional communication through mobile networks, mobile phones can also serve the information applications of mobile e-commerce, Internet of Things, media advertisements, etc., which operators hope to cut in, which is the focus of research in the field of mobile communication in recent years. Among them, mobile phone RFID technology has achieved breakthrough results and started commercial use.
The mobile phone RFID technology integrates the RFID chip into the mobile phone or mobile phone smart card (SIM/UIM) to realize the integration of the mobile phone function and the RFID function, and the user can brush the mobile phone to realize many applications such as financial service, shopping consumption, passenger service, identity authentication and the like. Since the mobile phone-based RFID technology cannot be supported by telecom operators, this paper will mainly focus on the implementation scheme, application status, existing problems and development trends of mobile smart cards (hereinafter referred to as mobile RFID smart cards) integrated with RFID radio frequency functions. .
2 mobile phone RFID smart card mainstream solution
At present, mainstream mobile phone RFID smart card solutions at home and abroad can be divided into two categories according to the operating frequency, namely 13.56 MHz solution and 2.4 GHz solution. The 13.56MHz solution can be further divided into an eNFC solution, a dual interface card self-contained antenna solution, and a dual interface card mobile phone customization solution. The following describes the four mobile phone RFID smart card solutions separately.
2.1 eNFC solution

The eNFC solution integrates the RF antenna and RF communication control functions into the mobile phone terminal, and puts the RFID data storage and data processing functions on the mobile phone smart card, and communicates between the card and the mobile phone through the SWP protocol to realize the integration of the RFID and the mobile phone.
The eNFC solution has been designated as an international standard by 3GPP and its technology is perfect. The 13.56Mhz frequency communication commonly used in the industry is adopted to facilitate the transformation and implementation of cooperative services. However, the eNFC solution must replace mobile phones and smart cards, and the cost is high; and currently supported mobile phone terminals and smart card products are few, and the industry chain is not mature enough. In addition, eNFC's patents are concentrated in the hands of foreign manufacturers Axalto and NXP, and the application of eNFC solutions on a domestic scale may encounter patent flaws.
2.2 Dual interface card mobile phone customization program

The dual interface card mobile phone customization solution integrates the RFID processing chip on the mobile phone smart card, and integrates the RFID coil on the mobile phone terminal, and the RFID smart card is connected with the coil of the mobile phone terminal through the C4 and C8 pins to realize the short-distance communication. This scheme adopts the 13.56Mhz frequency communication commonly used in the industry to facilitate the transformation and implementation of cooperative services. The terminal transformation only needs to realize the integration of the antenna and the mobile phone, and the modification is simple and the cost is low. The antenna is integrated into the terminal to improve card stability. The disadvantage is that it takes up C4, C8 contacts, and conflicts with large-capacity card applications in international standard applications, and still needs to customize the mobile phone terminal.
2.3 Dual interface card with its own antenna solution
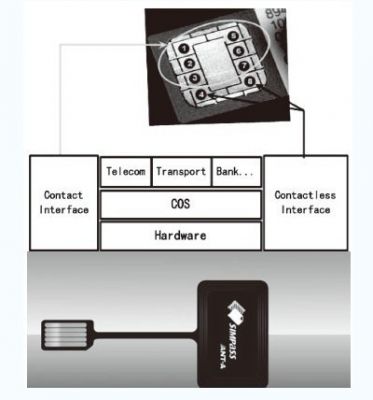
The solution integrates an RFID processing chip on a mobile phone smart card, and extracts an RFID coil from the smart card for short-range communication. The dual interface card self-contained antenna solution adopts the 13.56Mhz frequency communication commonly used in the industry, and does not need to replace the mobile phone, and the service implementation is convenient and fast. However, because the UIM card has a large RFID coil, the user is inconvenient to install and use, is relatively easy to damage, has a slightly poor card stability, and is poorly used. At the same time, it also occupies C4, C8 contacts, and conflicts with large-capacity card applications in international standard applications.
2.4 2.4G full card solution
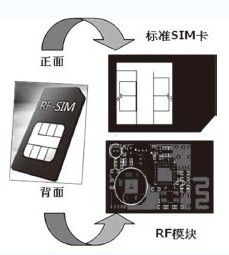
The 2.4G all-card solution is based on Bluetooth communication technology, integrates the Bluetooth RF chip into the smart card of the mobile phone, and performs on-site communication through technology such as distance control algorithm. It does not need to bring an antenna, and does not need to replace the mobile phone to realize the RFID card swiping function of the mobile phone. The implementation is convenient and fast. In addition to realizing the on-site card swipe function, the 2.4G full-card solution can also implement mid-range swipe applications and card reader applications according to business needs. However, since the 2.4G frequency band is not compatible with domestic and international financial and transportation on-site payment standards, new POS machines are needed for cooperative applications, and the cooperation is difficult, and the cost of equipment modification is relatively high.
3 Mobile phone RFID smart card industry application status
In the international arena, eNFC is mainly used as the standard. However, due to the lack of demand, there are few mobile terminals supporting eNFC. There are few commercial cases for using the eNFC solution for on-site credit card printing. There are many applications for mobile phone cards in Japan and South Korea, but because their mobile terminals use the card-in-one mode, they are not part of the mobile phone RFID smart card application mode.
4 Mobile RFID smart card problems
Since 2009, with the boom of mobile payment and mobile e-commerce, there have been many types of mobile RFID smart card types in China. The dual interface card solution and the 2.4G full card solution have all been innovative in mobile RFID smart card solutions. Development, and has a certain number of independent patents, it can be said that domestic research and application in the field of mobile phone RFID smart cards has been at the forefront of the international market, but because the industry has just started, there are still many problems. Mainly manifested in:
4.1 Standards are not uniform
The standard is not unified firstly, the operating frequency is not uniform. At present, the mainstream RF operating frequency has 13.60MHz and 2.4GHz two RF operating frequencies. The 13.56MHz frequency is currently widely used in many non-mobile RFID fields, but mobile RFID smart cards. If the frequency is 13.56MHz, the large antenna problem must be solved. The antenna is self-contained by the card, and the user's perception is poor and the stability is poor. When the antenna is placed in the mobile phone terminal, the mobile phone terminal must be customized, the development cycle is long, and it is difficult to scale commercial use in the short term. 2.4GH is ultra-high frequency, good penetration, no need for large antenna, can integrate RFID function in a smart card completely. The battle for work frequency has a long history, and the choice of work frequency directly affects the business model, business model and industrial chain cooperation. The problem is very complicated.
The standard is not uniform. The interface and protocol are not unified. The mobile phone RFID application includes cards and terminals (mobile terminal and POS terminal) domain, communication network domain, transaction processing domain and other fields. There is no unified interface between various domains. The definition and interaction protocol standards have led to the development of mobile RFID smart card products from various organizations that cannot communicate even in the same operating frequency range. Taking the card and the terminal domain as an example, the current transaction process and instruction standardization of the card and the terminal are not high, and the power, frequency offset, field strength and other indicators of the card and the terminal RF communication are not strictly agreed, resulting in the card may be at different terminals. Can not be recognized, or the card is unstable.
4.2 Multiple application bearer difficulties: Compared with ordinary mobile smart cards, RFID smart cards need to load communication applications, financial applications, school-enterprise applications, municipal applications, industrial card applications and other applications. One card carries multiple applications, and the following problems need to be improved, including: (1) Planning and managing multiple types of applications in the card to ensure flexible loading and smooth upgrade of applications. (2) Establish mutual isolation on the security domain between multiple applications to ensure that applications do not affect each other. (3) Large-capacity support, currently RFID smart card capacity is small, it is difficult to meet the needs of various application loading.
4.3 Low communication speed between mobile phones and smart cards: mobile RFID smart cards (including dual interface cards and 2.4G cards) for mainstream applications in the country, and air transaction data between mobile phones and smart cards are mainly carried out by means of data short messages. Limited by the rate of data short messages, it can not meet the application of dynamic loading and large-capacity file update of large data volume, and directly restricts the development of mobile terminal applications based on RFID smart cards, and can only realize simple applications by means of UTK menu. .
4.4 Security needs to be further improved: mobile phone RFID smart cards can now implement DES/3DES, RSA and other algorithms, and their chips can usually be certified by ELA4+ or ELA5+ security chips, which can meet the requirements of general small transaction security certification. However, for high-security applications such as large-value financial transactions and sensitive identification, existing mobile RFID smart cards are still difficult to support.
5 mobile phone RFID smart card development trend
Mobile smart cards have evolved from the original authentication module to the main carrier of mobile communication services and service innovation. Smart cards not only provide basic services such as user authentication and personal information management (such as address book and SMS service), but also provide mobile banking and credit cards. , e-money, transportation cards, stock trading and other services that require a higher level of certification. With the deepening of the transformation of telecom operators' comprehensive information services, smart cards will develop into integrated information service cards. In order to meet the needs of the development of integrated information applications, smart cards are mainly developed in the direction of convergence of RFID and SIM, large capacity, multiple applications, high security, and high card communication speed. Below, the author will discuss the development trend of mobile phone RF smart cards in terms of application, technology and industry.
5.1 Application level
The smart card of the mobile phone has security and personality, and the operator has controllability. At the same time, it is also the natural carrier of the identity of the telecom customer. The above characteristics determine that the smart card of the mobile phone will be directed to personal identity authentication, payment, mobile banking, mobile securities, and information inquiry terminal. Oriented development. The user owns a mobile phone RFID smart card, which can not only use the mobile phone as a comprehensive financial service terminal, but also enjoy flexible and convenient financial services and bank payment services. It can also enjoy the services of public transportation, company attendance, access control, canteen, etc. You can also enjoy convenient information services, such as life information inquiry, preferential information push and so on.
(1) Identity authentication application: The RF smart card is not only the user identity authentication module of the communication module, but also can be used as a module for digital authentication and digital signature. The personal identification and related information are stored in the user's RFID smart card, and the user's information is read and authenticated by the mobile phone RIFD technology, and the identification and authentication services such as access control, attendance and membership identification can be conveniently realized. The RF card can also be placed with the user's digitally signed certificate, and the digital certificate of mobile e-commerce and mobile office use can be realized through the certificate authentication of the CA certification center in the background to ensure the authenticity, privacy and integrity of the transaction. Non-repudiation.
(2) Mobile payment: The user can install the offline electronic wallet or online payment account in the RFID smart card. The wallet can be either the bank's electronic cash, bank card account, bus wallet, corporate campus canteen wallet, etc. The function of paying for the electronic wallet of the mobile phone can be realized conveniently on the contactless POS by the non-contact technology, and the transaction of the commodity and the related service purchase can be completed. The user can also conveniently manage the wallet through the mobile phone UTK menu, such as balance inquiry, transaction record inquiry, password modification, air storage and so on. In addition, users can purchase virtual electronic products, physical products, services, etc. through the mobile Internet, and realize remote payment through RF smart cards.
(3) Mobile banking: Mobile banking provides customers with a comprehensive financial service platform. The platform will solidify the online banking function of the bank into the telecom mobile phone menu in the form of a proprietary program, or it can be installed into the mobile phone through download. And through the WPKI technology, the user's digital signature certificate is placed to ensure the security of the mobile banking. Users can use the platform to realize functions such as transfer, remittance, inquiry, payment, and deposit. After the bank ATM module is replaced, the mobile phone can be cashed on the ATM. The close integration of mobile banking and mobile payment services will create an integrated financial service platform with mobile terminals and mobile RFID smart cards as the core to provide customers with a full range of financial services.
(4) Mobile securities: The mobile securities business is a new business of cooperation between telecom operators and brokerages. Customers can use mobile client software to complete market inquiry and stock trading, providing users with timely, comprehensive and authoritative financial information. Individual stock reviews, market analysis, gathering of famous experts strategy, news analysis, hot perspective and other professional information. At the same time, customers can conveniently conduct transactions and inquiries of various securities types in Shenzhen and Shanghai through mobile phones. In order to ensure the security of customer transactions, WPKI technology is used to place the customer's digital signature in the RFID smart card, and the digital signature verification of the mobile phone and the certification center of the brokerage backstage ensures the uniqueness, security and non-repudiation of the customer transaction.
(5) Information inquiry: The mobile phone RFID smart card can realize the information service such as the inquiry of life information, the download of the game, and the download of the commodity coupon through the UTK menu. Users can also update and manage STK/UTK menus in real time through OTA technology, and set their favorite menu types more autonomously, making it easier to select and locate their favorite value-added services. By operating the OTA platform business, mobile operators can formulate a set of specifications for platform management, user management, SP management, service management, and billing management. Together with SP, they can create a complete mobile value-added service value chain and provide users with more More and better value-added services.
5.2 Technical level
In order to meet the needs of the above-mentioned comprehensive information application development, mobile smart cards must first solve two core technical problems: one is the fusion of RFID contactless technology and the original contact technology of SIM/UIM card, and the other is because the mobile smart card needs to be loaded. The problem of multiple applications and multiple security domains brought by multiple applications. Around these two core issues, mobile smart cards also need to address capacity issues, machine card rate issues, security issues, and smart card readhead technology.
(1) The fusion of RFID contactless technology and SIM/UIM card original contact technology
The integration of RFID contactless technology and SIM card contact technology is a core issue in the development of mobile payment technology. The development of mobile payment services is based on the premise of the combination of contact and non-connection. Through the combination of the two, the traditional RFID technology is realized as the application of near-field payment, access control, attendance, public transportation, etc., and also satisfies the functions of the traditional mobile phone, and more importantly, through the combination of the two. The new business blue ocean, specifically, through the STK/UTK menu of the mobile phone, can conveniently query the balance, transaction records, and other related information on the smart card, and can realize the refill function of the wallet through the air storage, and solve the original Bank cards, bus cards, enterprise cards, etc. cannot directly interact with customers in real time and facilitate management.
(2) Multi-application and multiple security domain management
At present, the mobile smart card adopted by the operator is basically a single application card, and the multi-application smart card is still in the trial stage. Single-application mobile smart cards can only have one application, and can not directly add additional applications, and the applications we use in mobile stocks, mobile banking, etc. are all implemented by STK/UTK. The future of smart cards is moving towards the goal of multiple applications. The architecture realizes the separation of platforms and applications. The above mentioned non-telecom applications or telecom value-added applications can be fully built on this platform, and each application can follow its own Industry specifications, such as EMV, PBOC, and social security regulations, do not require the installation of other cards.
Multi-application mobile phone RIDF smart cards must support multiple logical channels. The logical channel is used for parallel application of smart cards for different applications of 3G user terminals. In addition to the basic logical channel 0, there are three logical channels, and at least one must be supported. The basic logical channel 0 is always present and open. After the card is reset, the logical channel 0 is used by default, and other logical channels can be opened (or closed) through the channel. The commands on each logical channel are independent of each other, with no interleaved commands and responses.
Since smart cards are loaded with not only telecom applications, but also other industries, for security reasons, all industries have their own security key system, which requires smart cards to have security domain management functions. The multi-security domain architecture provides a mechanism by which to define which commands are executed under what conditions and what conditions are met for access to the file. The content of the security system mainly includes the following parts:
Security attribute: It is a collection of several access rules.
Access rules: Contains an access mode and one or more security conditions. It mainly describes what security conditions should be met when making different access to a file.
Access Mode: Indicates which actions the security condition applies to. It mainly describes the access methods of the file, that is, which access commands can be used for the file.
Security Conditions: Security conditions indicate what security-related processes are to be met before executing a command on a file. It mainly describes which related security conditions or procedures should be met when accessing files using access commands.
(3) High security technology: When mobile RFID smart cards are used in personal identity authentication, mobile banking, mobile securities, etc., security is the most critical factor in business. In order to provide high-reliability security for applications, future mobile RFID smart cards will integrate security chips to implement WPKI (“Wireless Public Key Systemâ€) security mechanism to meet the reliable and high-security authentication requirements of financial institutions. WPKI is the "wireless public key system", which is a key and certificate management platform system that introduces the PKI security mechanism in Internet e-commerce into the wireless network environment and follows the established standards. It is used to manage the use in the mobile network environment. The public key and digital certificate effectively establish a secure and trustworthy wireless network environment.
WPKI is not a new PKI standard, it is an optimized extension of the traditional PKI technology applied to the wireless environment. It uses an optimized ECC elliptic curve encryption and compressed X.509 digital certificate. It also uses the certificate management public key to authenticate the user's identity through a third-party trusted authority, the Certificate Authority (CA), to achieve secure transmission of information.
(4) BIP protocol: There is also a dynamic service download/delete function in the SIM/UIM card of the 2G network, but all downloads are performed through the SMS channel, the data carrying capacity is small, the stability is poor, and the download capacity is large. Application business. In order to meet the needs of multi-application management and downloading large data volume interactions in the future, mobile RFID smart cards must support the BIP (Bearer Independent Protocol) protocol. Through the BIP protocol combined with the USAT application, the mobile terminal allows transparent data transmission between the mobile smart card and the remote server. The BIP protocol is more conducive to the transmission of high-speed mobile data services, making downloading various business data easier and faster.
(5) High-capacity demand: As more and more applications are carried on RFID smart cards, the requirements for smart card capacity are also increasing. At present, the space used by mainstream dual-interface payment cards is 80k. In cooperation with banking services, it takes about 30K to complete a complete PBOC2.0 application. If other functions are added, it may take more than 50K. Make other apps unloadable. Future RF smart cards not only need to carry payment-related applications, but also information query applications, identity authentication applications, and the mega-level capacity requirements are more urgent.
(6) Card reader function: The future development of RF smart card is not only to be read as a card, but also to support the reading of other cards as a read head. The function of the smart card as a card reader will be widely used in the development of the Internet of Things. For example, in intelligent transportation, the police can easily read the information of the vehicle by using the mobile phone. In the smart home, the customer can conveniently read through the mobile phone. Take information about home appliances. At present, the RFID smart card technology that supports this function is only the 2.4G full card solution and the eNFC solution.
5.3 Industry development
(1) Frequency standard issue: At present, the state has begun to formulate national standards for mobile payment, taking into account various factors such as technology maturity, security, patent protection, and industrial chain status. Once the national standards are formulated, existing mobile phone RFID technologies are available. The solution will be gradually unified and integrated. Based on the consideration of industry versatility, the author predicts that the national standard for mobile payment is more likely to choose 13.56MHz. The 2.4G RFID smart card can be technically integrated with the 13.56M eNFC/SWP solution, and it can be applied in special occasions such as medium and long distance interactive services by utilizing its characteristics of medium and long distance.
(2) RFID smart card system problem: The original mobile phone smart card is basically a Native card. The native card operating system is private to the card merchant. The application development and loading are not flexible, and it is difficult to meet the requirements of the mobile phone RFID smart card multi-application. Because the JAVA card is universal, the application can be dynamically loaded, which greatly facilitates the development and loading of the card application. It satisfies the requirements of multiple security domains for RF smart cards. In the future, mobile RFID smart cards will gradually migrate to JAVA cards.
Because the cost of JAVA card is relatively expensive, the program has higher requirements on chip hardware (such as chip RAM space, card capacity, etc.), and the card response is slow. Although foreign operators have started to issue cards in batches, in domestic, JAVA card is in communication. The application of the industry has just started, and the relevant card suppliers are not enough in terms of technical reserves. The migration of mobile phone RFID smart cards to JAVA cards requires a certain process.
The accessories are very important in using and installing, so we offer the driver,controller,Mounting Brackets,and led strip caps.Use the driver to support the led strip lights,because the led strips are low voltage. If there needs color change or adjusting brightness,the RGB controller or dimmer can make it real.In order to make the installation easy, the unique brankets are optional.Each evenstrip has matched bracket.If the length of led strip needs to cut short,use the plastic end caps to keep waterproof.
Strip Light Accessories,Waterproof Led Driver,Led Strip Light Controller,Led Strip Cap
Guangdong Kamtat Lighting Technology Joint Stock Co., Ltd. , http://www.ip68ledstrip.com