POP3 is fully named "Post Office Protocol - Version 3", which is "Post Office Protocol Version 3". Is a member of the TCP/IP protocol suite defined by RFC1939. This protocol is mainly used to support the use of clients to remotely manage email on the server. The POP3 protocol that provides SSL encryption is called POP3S.
The POP protocol supports "offline" mail processing. The specific process is: the mail is sent to the server, the email client invokes the mail client program to connect to the server, and downloads all unread emails. This offline access mode is a store-and-forward service that sends mail from a mail server to a personal terminal machine, typically a PC or MAC. Once the mail is sent to the PC or MAC, the mail on the mail server will be deleted. However, most of the current POP3 mail servers can “download only mail, and the server does not delete itâ€, which is the improved POP3 protocol.
POP3 operation guide:The server allows mail clients that conform to POP3 (Post Office Protocol, Version 3 Mail Delivery Protocol, Version 3) to connect to the Imail server. These email client software includes Outlook Express, Outlook, Netscape Messenger or Communicator, Eudora, Pegasus, NuPOP, Z-Mail, FoxMail, TheBat, Kmail, and Unixmail [2] .
POP3 clients usually use off-line offline access to the mail server, access the mail server regularly, download the mail to the client's computer, and then disconnect from the server. In general, mail is temporarily stored on the server. When the client downloads the mail, they will be deleted by the server and will not be retained. For those who always read emails on the same computer, this method is very suitable. Another way, called "online" online, is that the mail client always stays connected to the server. The mail is kept on the server. The client does not download the mail to the client. The user can read the mail kept on the server online. Users who often use different computers are suitable for this approach. The ImailPOP3 service can operate as a Windows NT service, completely hidden, or it can run in some interactive way. The service will always run even if you log out of the system. IMail also provides another access method, IMAP4 (InternetMessageAccessProtocolVersion4). The IMAP4 service provides both "online" and "offline" access methods. Logging On Logging On By default, the POP3 service uses the system account to log in to the system. You can change this login method:
1. In the control panel, start the Services applet.
2. Select the IMailPOP3 Server service and click Startup.
3. (Optional) Select the Startup Type you want.
4. In LogOnAs, select the correct login account: IMailServerSystemAccount. If you have a mail host that uses the Windows NT user database as the Imail user database, then you need to use that account. AllowServicetoInteractwithDesktop. When using this account, any user who logs in to the system will have an icon for Imail on the desktop.
ThisAccount. In this way, if your host does not use the Windows NT user database, you can enter your desired user account; confirm that the account is a host administrator. If you have an email host that uses an external database, verify that the account can access an external database.
Configuring the POP3 Server to Configure the POP3 Server How to Configure the Pop3 Server:
1. In the IMail Administrator, select "localhost" in the left panel.
2. Select the "Services" directory and click on the POP3.POP3 panel.
3. Enter the options described below to configure the POP3 service.
4. Click the button Apply to save the settings.
5, stop the service, wait 5-10 seconds and then restart the service. When you click the button Stop/Start, the settings change is automatically saved.
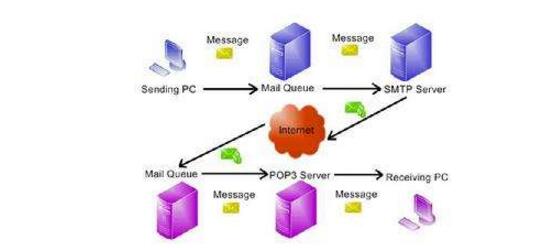
Simple Mail Transfer Protocol (SMTP) is a simple mail transfer protocol. It is a set of rules for sending mails from a source address to a destination address. It controls the relaying mode of a mail. The SMTP protocol belongs to the TCP/IP protocol suite and it helps each computer find the next destination when sending or relaying mail. Through the server specified by the SMTP protocol, the E-mail can be sent to the recipient's server. The entire process takes only a few minutes. The SMTP server is an outgoing mail server that follows the SMTP protocol and is used to send or forward outgoing emails.
It uses a reliable data transmission service provided by TCP to transmit mail messages from the sender's mail server to the recipient's mail server. Like most application layer protocols, SMTP also has two ends: a client that executes on the sender's mail server and a server that executes on the recipient's mail server. The SMTP client and server side run on each mail server at the same time. When a mail server is sending mail messages to other mail servers, it is running as an SMTP client.
SMTP working process:Simple Mail Transfer Protocol (SMTP) is a text-based email transmission protocol that is used in the Internet to exchange messages between mail servers. SMTP is an application-level service and can be adapted to various network systems.
The commands and responses of SMTP are based on text and are in the unit of command behavior. The newline character is CR/LF. The response message is generally only one line, starting with a three-digit code followed by a brief text description. SMTP needs to establish a connection, send mail, and release the connection in three phases. Specifically:
(1) Establish a TCP connection.
(2) The client sends a HELO command to the server to identify the sender's own identity, and then the client sends the MAIL command.
(3) The server responds with OK indicating that it is ready to receive.
(4) The client sends an RCPT command.
(5) The server indicates whether it is willing to receive mail for the recipient.
(6) After the negotiation is completed, send an e-mail and use the command DATA to send the input.
(7) End this transmission and exit with the QUIT command.
The SMTP server routes email based on mail exchange (MX) records in the DNS. When the e-mail system sends an e-mail, the mail server is located according to the address suffix of the recipient. SMTP performs functions such as editing, receiving, and reading of mail through user agents (UAs); mails are delivered to destinations through the mail transfer agent (MTA).
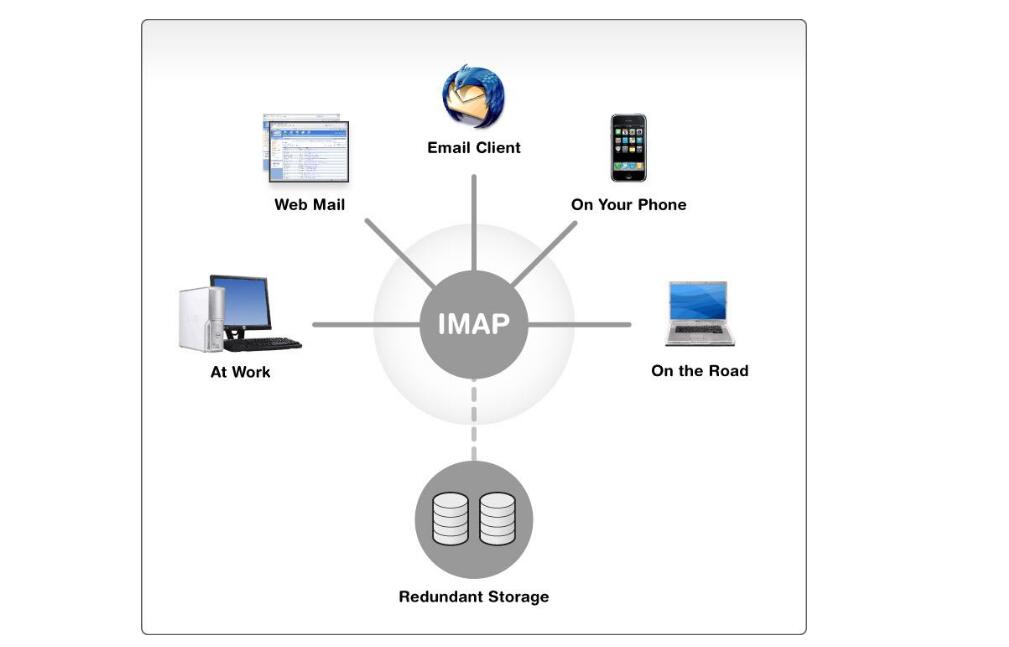
The Internet Mail Access Protocol (IMAP) was formerly known as the InteracTIve Mail Access Protocol. IMAP is an email acquisition protocol developed by Stanford University in 1986. Its main role is that e-mail clients (such as MS Outlook Express) can obtain e-mail messages from mail servers, download e-mails, and so on. The current authoritative definition is RFC3501. The IMAP protocol runs above the TCP/IP protocol and uses 143 ports. The main difference between the POP3 protocol and the POP3 protocol is that users can download all the emails without having to download all the emails. The client can directly operate the email on the server.
Imap features:Similar to the POP3 protocol, IMAP (Internet Message Access Protocol) also provides user-oriented mail collection services. The common version is IMAP4.
IMAP4 has improved the deficiencies of POP3, users can browse through the letter header to decide whether to receive, delete and retrieve specific parts of the mail, you can also create or change the folder or mailbox on the server. In addition to the offline operation mode of the POP3 protocol, it also supports online operation and disconnection operation. It provides users with the ability to receive mail from the mail server, server-based information processing, and shared mailbox functions. The offline mode of IMAP4 is different from POP3. It does not automatically delete the mails that have been taken out on the mail server. The online mode and disconnected mode also access the mail server as a “remote file serverâ€, which is more flexible and convenient. IMAP4 supports multiple mailboxes.
These features of IMAP4 are ideal for users who operate emails between different computers or terminals (for example, you can operate the same mailbox on email agents on mobile phones, PADs, and PCs) as well as those who use multiple mailboxes at the same time.
Imap function:Support connection and disconnection of two modes of operation. When using POP3, the client will only connect to the server for a period of time until it downloads all new information and the client disconnects. In IMAP, the client is always connected to the server as long as the user interface is active and downloading information content is needed. For users with many or large e-mails, using the IMAP4 mode can achieve faster response times. Supports multiple clients connecting to one mailbox at the same time. The POP3 protocol assumes that the current connection to the mailbox is the only connection. In contrast, the IMAP4 protocol allows multiple users to access the mailbox simultaneously while providing a mechanism for the customer to perceive the actions of other users currently connected to the mailbox. Supports access to MIME parts and partial access in messages. Almost all Internet mail is transmitted in MIME format. MIME allows messages to contain a tree structure whose leaf nodes are all of a single content type rather than a combination of leaf types. The IMAP4 protocol allows the client to obtain any individual MIME part and to obtain some or all of the information. These mechanisms allow the user to browse the message content without having to download the attachment or to browse while acquiring the content. Supports maintaining message status information on the server.
By using the flag client defined in the IMAP4 protocol, the message status can be tracked, such as whether the message was read, replyed, or deleted. These identifiers are stored on the server, so multiple customers accessing one mailbox at different times can sense what other users are doing. Support for accessing multiple mailboxes on the server. IMAP4 clients can create, rename, or delete mailboxes on the server (usually presented to users as folders). Support for multiple mailboxes also allows the server to provide access to shared and public folders. Support server-side search. IMAP4 provides a mechanism for customers to enable customers to request servers to search for information that meets multiple criteria. Under this mechanism, the client does not need to download all the information in the mailbox to complete these searches. Supports a well-defined extension mechanism. Drawing on the experience of earlier Internet protocols, IMAP's extension defines a clear mechanism. Many extensions to the original protocol have been proposed and widely used. Whether using POP3 or IMAP4 to get messages, the client sends using the SMTP protocol. The mail client may be a POP client or an IMAP client, but it will use SMTP.
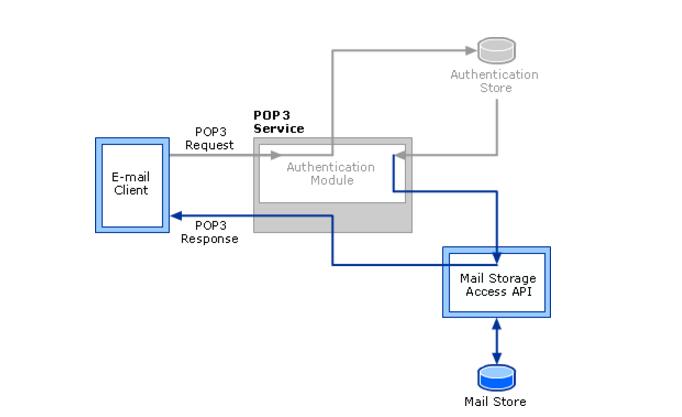
POP3 stipulates how to connect a personal computer to the Internet's mail server and download e-mail's electronic protocol. It is the first offline protocol standard for Internet e-mail. POP3 allows users to store mail from the server to the local host (ie, their own computer) and delete the mail stored on the mail server. The POP3 server follows POP3. The protocol's incoming mail server is used to receive emails.
The POP3 protocol allows e-mail clients to download mail on the server, but the client's operations (such as mobile mail, tags, etc.) will not be fed back to the server, for example, the client will receive 3 e-mails in the e-mail and move it. To other folders, these emails on the Mailbox server have not been moved at the same time.
IMAP provides two-way communication between webmail and e-mail client. The client's operation will be fed back to the server. The operation on the e-mail and the e-mail on the server will also take corresponding actions. At the same time, IMAP provides a convenient email download service like POP3, allowing users to read offline. The summary browsing function provided by IMAP allows you to make a decision on whether to download after you have read all the message arrival time, subject, sender, size and other information. In addition, IMAP better supports access to new mail from multiple different devices at any time.
SMTP It is a set of specifications for the transmission of mail from the source address to the destination address, which controls the way in which mail is relayed. The SMTP protocol belongs to the TCP/IP protocol suite and it helps each computer find the next destination when sending or relaying mail. The SMTP server is a sending mail server that follows the SMTP protocol.
SMTP authentication simply means that you must log in to the SMTP server after you provide your account name and password. This makes the spammers inaccessible. The purpose of adding SMTP authentication is to protect users from spam.
The full name of IMAP is the Internet Mail Access Protocol, which is an interactive mail access protocol. It is one of the standard email access protocols similar to POP3. The difference is that when IMAP is enabled, the emails you receive from email clients are still kept on the server. At the same time, operations on the client are fed back to the server, such as deleting emails, marking reads, etc., on the server. Mail will do the corresponding action. Therefore, regardless of the login email from the browser or the client software login email, the email and status are the same.
The Screen Protector has a self-healing technology that can automatically eliminate small scratches on the Protective Film within 24 hours. Significantly reduce dust, oil stains and fingerprint smudges, anti-scratch.
The Screen Protection Film is very suitable for curved or flat screens. The Soft Hydrogel Film perfectly matches the contour of your device. Will not affect any functions of the phone.
The Ultra-Thin Protective Film with a thickness of only 0.14mm uses 100% touch screen adaptive screen touch screen technology, complete touch screen response, high-tech technology makes the screen touch to achieve zero delay, ultra-thin material brings you "realism".
The Protection Film has excellent clarity and incredible toughness, providing a high level of clarity and a glass-like surface, highlighting the sharpness of the most advanced smartphone display images and bright colors.
If you want to know more about Self Repair Screen Protector products, please click the product details to view the parameters, models, pictures, prices and other information about Self Repair Screen Protector.
Whether you are a group or an individual, we will try our best to provide you with accurate and comprehensive information about the Self Repair Screen Protector!
Self-healing Protective Film, Self-repairing Screen Protector,Self-healing Screen Protector, Self-Healing Hydrogel Film,Hydrogel Film Screen Protector
Shenzhen Jianjiantong Technology Co., Ltd. , https://www.jjtphonesticker.com