The level of intelligence of mobile phones continues to increase, not only because they can recognize faces in photos and make calls by voice commands. The way they use energy is also smarter, meaning that they can run longer on a single charge, allowing you to fully enjoy the game and social fun. Here are six main reasons why your phone's Battery life is longer.
Better wireless management
In the past, we needed to turn off WiFi, 3G and GPS to extend the phone's battery life. We don't have to do this now, because the software in the phone can be managed more efficiently, ensuring that the wireless connection is only used when needed.
Other changes have occurred in the wireless connection. Bluetooth Smart (also known as Bluetooth Low Energy)'s low-power protocol further increases energy efficiency, allowing sensor components to run on a lithium coin cell battery for up to a year. As a result, Bluetooth Smart is critical to designing a wide variety of wearable devices, including smart devices that require monitoring information to be sent to smartphones, such as pedometers and heart rate monitors.
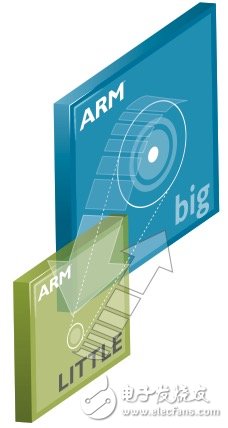
big.LITTLE processor architecture
One key to extending the current battery life of mobile phones is to ensure that the processor is running current software, such as mobile applications, and will not be overkill. High-performance gaming and high-definition video require an application processor to meet their intensive computing requirements, but most of the time, the software running on the phone does not require the fastest processor.
The big.LITTLE architecture used by many phones monitors which software is running. If a high-speed (often high-power) processor is not needed, the code running on it will be moved to a lower-performance kernel, and the other cores will be shut down. The high speed and more power-hungry processor will only start again if the workload is too strong.
Sensor hub
Many mobile phones now have sensor hubs that continuously collect data from many (sports) sensors inside the phone. These very low-power, always-on processors are responsible for monitoring and storing data from accelerometers and other sensors, and then only need to wake up the more power-hungry application processor when analyzing and displaying the results.
Fine voltage
Smart use of processing and wireless operation saves power, and while using these features, you can further minimize its power consumption by carefully adjusting the supply voltage it requires. There is a square relationship between voltage and power in most circuits. Therefore, as long as the conditions permit, it is worthwhile to lose the voltage of 0.1V, because this will greatly help the power consumption reduction.
This produces a series of voltage rails that are less than 1.5V for powering the processor, memory, and other peripheral circuits that can dynamically rise and fall directly in accordance with the amount of work the handset needs to perform. For example, when the phone is idle, it is possible to reduce its supply voltage and then increase the voltage when high performance is required. The result is that the phone is always looking for the lowest possible voltage for each of its subsystems, all managed by a complex power management integrated circuit (PMIC).
Smarter display
Display screens used to be one of the most power-hungry components of mobile devices, the main reason being backlighting. The solution is to minimize the brightness of the backlight without reducing the visual quality. The phone measures the ambient light and reduces the brightness of the backlight when the light is sufficient. The power management IC ensures fine-tuning of the backlight power without flicker or other problems, but the main reason for the reduced power requirements is the increased efficiency of the WLED.
PMIC optimization
In addition to the need to handle many voltage outputs and their variations, the PMIC itself has changed; traditionally, the voltage of many independent power supplies required to convert the battery voltage into various chips (circuits) inside the handset is mainly for high load conditions. Optimized for efficiency, paying less attention to efficiency under light load conditions. This traditional approach helps ensure that mobile devices do not overheat when performing intensive operations. However, in an always-on environment, data processing continues in the background, so high efficiency is required under various load conditions.
The current consumption of low load and high load may differ by several orders of magnitude, for example, tens of milliamps from the standby of the device, to more than 10 amps when starting the processor and starting to process data as quickly as possible, and then down to continuous video decoding Or do some hundreds of milliamps for a Facebook update. Today's PMICs use advanced digital technology to deliver greater than 90% efficiency from low to high loads and many voltage rail conditions, helping handsets stay cool and extend battery life on one charge – the latest in mobile phones It is well proven.
Zhejiang Baishili Battery Technology Service Co,.Ltd. , https://www.bslbatteryservice.com